In medical treatments today, patients might receive a pint of whole blood or they may receive just certain components of the blood required for treating their particular condition. This treatment approach, known as blood component therapy, makes it so several patients can benefit from a single pint of donated blood. Here, you’ll learn about the different components of blood, blood storage temperature and how the red blood cells, platelets and blood plasma are stored and transported.
Table of Contents
- Components of Whole Blood
- How Are Red Blood Cells, Platelets and Blood Plasma Stored?
- How Is Blood Transported?
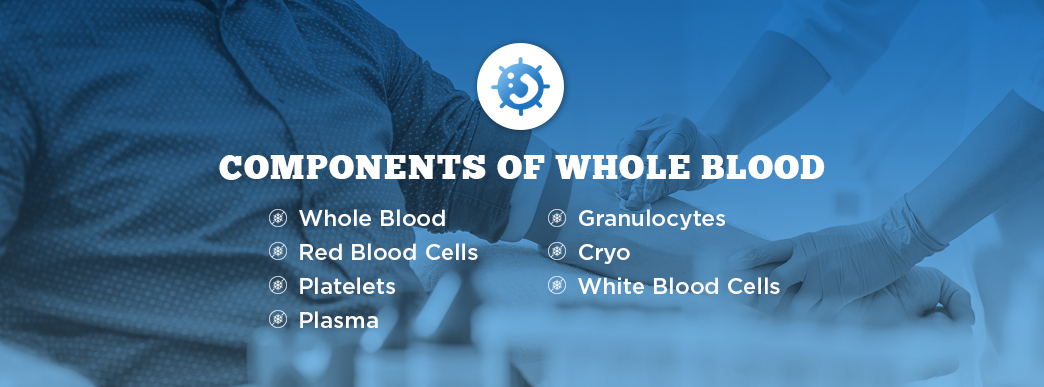
Components of Whole Blood
The transfusable components you can get from donated blood are red blood cells, platelets, plasma, granulocytes and cryoprecipitated AHF (cryo). An additional component, white blood cells, is often removed before transfusion from donated blood.
1. Whole Blood
Whole blood contains platelets, red cells and white cells. It’s the most common, simplest form of blood donation. Because it may be used for helping several people when it’s separated into its certain components of plasma, red cells and platelets or because it may be transfused in its original form, it’s also the most flexible. Doctors use whole blood for treating patients who require all blood components, like those who have sustained substantial blood loss because of surgery or trauma.
2. Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, provide blood with its distinctive color. Your bone marrow produces it. The red blood cells deliver oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body and then, as you exhale, take the carbon dioxide back to your lungs.
3. Platelets
Platelets are colorless, small cell fragments in your blood with a primary function of sticking to your blood vessel lining, helping to prevent or stop bleeding. Your bone marrow makes platelets.
4. Plasma
Blood plasma is your blood’s liquid component that holds your blood’s cellular components in suspension. It’s a slightly cloudy liquid with a color that varies from bright green to pale yellow from person to person. Plasma makes up about 55% of your total blood volume. It doesn’t contain clotting factors or blood serum.
Blood plasma is 90% water. The other 10% is substances dissolved in water:
- Electrolytes
- Plasma proteins
- Low-molecular substances, such as vitamins, hormones and trace elements
An essential task of your blood plasma is to work like a medium for cellular components transportation.
5. Granulocytes
Granulocytes are a form of white cell that can protect against infection. They surround and destroy invading viruses and bacteria. They can be used in treating infections that aren’t responding to antibiotics. Granulocytes are gathered through an automated process known as apheresis. But, they need to be transfused within 24 hours of being donated into the patient.
6. Cryo
Cryo is a part of plasma rich in clotting factors, including fibrinogen and Factor VIII. These clotting factors decrease the loss of blood by helping to stop or slow bleeding caused by injury or illness.
7. White Blood Cells
Also called leukocytes, white blood cells are one of your body’s defense systems against disease. Some produce antibodies against viruses and bacteria, some destroy bacteria and some fight malignant disease.
But, although your white cells help you stay healthy, they can be dangerous if you receive donated blood since leukocytes might carry viruses that could suppress your immune system and release toxic substances into your body. To prevent these negative reactions, transfusable blood components often don’t contain leukocytes. They’re removed through a process referred to as leuko-reduction.
How Are Red Blood Cells, Platelets and Blood Plasma Stored?
What happens to donated blood and how is donated blood stored? Here you’ll learn the answer to the questions for red blood cells, platelets and blood plasma.
How Are Red Blood Cells Stored?
Specialists prepare red blood cells from whole blood by taking out the plasma. Red blood cells have an up to 42-day shelf life, depending on what anticoagulant was used. They must be stored and transported through refrigeration. However, specialists can treat and freeze them for 10 years or more.
How Are Platelets Stored?
Specialists use a centrifuge to prepare platelets and separate plasma rich in platelets from donated whole blood. Platelets from a few different donors are then combined, making one transfusable unit. Or, specialists can obtain platelets using an apheresis device that:
- Draws blood from the arm of the donor
- Separates the blood into its various components
- Keeps some of the platelets
- Returns the blood remaining back to the donor
A single donor, using this process, can contribute around four to six times the amount of platelets than with a unit of platelets derived from whole blood donation.
The specialists store the platelets for up to five days at room temperature. They need to constantly provide gentle agitation to the platelets to keep them from clumping.
How Is Blood Plasma Stored?
With blood plasma storage, after it’s been dissolved in water or thawed for the purpose of injection, the plasma can’t contain gelatinous or solid substances.
Blood plasma isn’t a sterile product. All units of plasma contain a small number of pathogens and microorganisms. But, since specialists store blood plasma in hermetically sealed containers where it’s frozen, it doesn’t require sterile storage. Frozen blood plasma is then transported to where it needs to go.
Pharmaceutical freezer unit technology through Klinge Corporation is constantly tested to provide the most efficient and effective freezer units for your container storage and transporting needs.
The plasma proteins’ activity in blood plasma can affect the plasma’s quality. Excessive temperatures during storage and transportation cause this activity to decrease, thereby degrading the final product’s quality.
Therefore, industrial plasma, after being donated, should be stored for a maximum of 36 months. On the other hand, transfusion plasma, after being donated, can’t be used beyond 24 months.
How Is Blood Transported?
When blood plasma is stored and transported, the “Good Distribution Practices” (GDP) and “Good Manufacturing Practices” (GMP) must be observed together with any applicable local jurisdictional standards and requirements. These practices and acts stipulate the standard operating procedures (SOPs).
Each manufacturer draws up the SOPs that will typically become part of the framework agreements with the carriers and shipping agents. An essential requirement is the cleanliness of warehouses and the means of transport.
If the SOPs deviate in any way or if there is any damage discovered during transportation, the manufacturer’s quality department must analyze and assess the damage or deviation. The quality department will then decide if any damage or deviation has occurred within acceptable tolerances.
Contact Klinge Corporation for Your Specialized Freezer and Refrigerated Transport Container Needs
Now that you know the different blood components, how long can blood be stored and how it’s stored and transported, it’s time to find a superior refrigerator and freezer container solution for your transportation needs.
The Klinge Corporation is a world-class innovator in the industry of refrigerated transportation. We provide outstanding transport container solutions for various industries. Contact us today to learn more about our specialized freezer and refrigerator transport containers, such as our container cooling units, tank containers, freezer shipping containers, and pharmaceutical containers.